If you are an ex-smoker, you are probably wondering how long does nicotine remain in your system.

High nicotine levels can affect your ability to receive life insurance policies at current rates, according to a study published online by the New England Journal of Medicine. People who smoke or have chronic diseases are more likely to be deemed “high risk” and pay more for life insurance than people without these health problems. The reason is that smokers are considered more dangerous to their lives than people with less risky lifestyles.
Cigarettes contain over 400 different chemicals. Some chemicals are carcinogenic or toxic, some are anti-carcinogenic, others affect the respiratory tract or heart, and still others are just harmful to your health overall. But nicotine itself is not carcinogenic, nor is it toxic. So, why are smokers considered high risk, and why do insurers increase their life insurance rates?
The answer is that smokers have much higher cotinine levels in their system than non-smokers do. This chemical is what determines how long nicotine stays in your blood.

Higher levels of cotinine in the blood mean higher nicotine retention in the body. This is how life insurance companies to determine your premiums.
Nicotine is stored in various organs of the body, including the lungs, heart and brain. When nicotine breaks down, the toxins released in the bloodstream escape into other parts of the body. High cotinine levels in the blood mean high nicotine retention in the brain.
Because nicotine and cotinine are both metabolized in the brain, a person who has low nicotine and high cotinine levels in the bloodstream is considered “low risk.” But if they have either type of chemical in the brain, they are considered high risk.
For a smoker, cigarette smoking is a known cancer risk factor. Smoking not only causes damage to the lungs but also increases the risk of heart disease and certain cancers of the esophagus, pancreas, liver, and colon. Excess tobacco use can also cause kidney failure and Alzheimer’s disease.
Smokers who quit smoking often experience a reduction in their mortality rates. But many people who try to quit are put off because they do not understand how long does nicotine remain in your system.
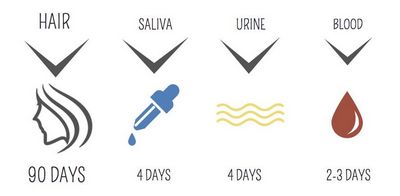
The best way to answer this question is, “How long does cigarette smoking stay in your bloodstream?” If you are not interested in smoking cigarettes at all, then you will want to know the answer to this question as well. To find out how long does smoking last in your body, go to your local drugstore and take a saliva test.
The saliva test can give you the answer to this question with a saliva sample taken from the mouth. This test will provide a snapshot of how long nicotine remains in your blood.
If you have not yet completed the saliva test, you may want to consider taking one before you quit smoking. This way, you will be able to determine how long does nicotine stay in your blood after you stop. You will know whether or not you should start smoking cigarettes to reduce or eliminate your risk.
So how long does smoking stay in your system? The answer to this question will help you decide if it is time to start to quit smoking or if you should wait until you are healthier. If you smoke cigarettes daily and you do not smoke to reduce or eliminate your risk of cancer, you probably should continue smoking.
If you are a smoker, the best way to find out how long does nicotine remain in your system is by using the saliva test. This simple test will answer this important question.
If you do not smoke, quitting is much easier than quitting with no cigarette smoking. Quitting will require that you take the extra step to quit, and most people quit smoking successfully after just one attempt.